|
From the evolution of integration-introduction to
 |
|
 |
|
 One wants to meet different market needs of general-purpose interface Bus standards, can continue to upgrade transmission speeds and greater bandwidth, to achieve speed, capacity, quality and other multivariate integration, enhance the effectiveness of desire?
One wants to meet different market needs of general-purpose interface Bus standards, can continue to upgrade transmission speeds and greater bandwidth, to achieve speed, capacity, quality and other multivariate integration, enhance the effectiveness of desire? |
|
 |
|
 |
Bus (Bus) between the CPU, Memory and I / O is used to bring together a hardware interface to pass the information program on the motherboard. Like its English name, the motherboard if criss-cross the city, the bus is able to shuttle bus transfer station, the bus is in accordance with the specific route scheduling traffic in planning Gexinggese electronic bits. In general, through the bus to the installation of a variety of adapters, internal various elements of the system will be able to transfer information program to link adapter with external peripherals. Common Bus is connected to each adapter ISA, PCI, AGP, and the connection of external USB and IEEE1394, etc..
PC system bus can be divided into the address bus (Address Bus; store data in RAM is used to specify the address), data bus (Data Bus; sending data back and forth between the MPU and RAM), control bus (the control Bus; the the MPU control unit signals sent to the peripheral device to run the program), the expansion bus (expansion bus; connection slot and the PC so the adapter to become a part of the PC), local bus (Local Bus; replace the high-speed transmissionexpansion Bus; often used to connect the MPU and video card slot).Bus Specifications usually distinction bandwidth (width), depending on the data width operation clock, every time the size of the amount of data that can be passed on behalf of the data width, while the clock represents the number of transmission of information per second, can perform the operation.
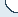
IBM introduced the world's first the included Intel8088 the PC / XT, began the era of the PC Bus pursuit transmission speed and capacity. IBM introduced the for personal PC compatible ISA Bus (Industry Standard Architecture Bus; Industry Standard Architecture bus), the transmission speed of 38Mbps (bandwidth 4.8MB / s 8bits/4.77MHz); 1984, IBM introduced the PC / AT after, the speed increased to 128 Mbps (16MB / s 16bits/8.33MHz) ISA advantages corresponding adapter design is simple, the disadvantage is that the transmission speed is slow.In 1987, IBM introduced the IBM PS / 2, and its development of a 32-bit MCA Bus (Micro Channel Architecture), but because IBM did not open MCA details of the technical standards and the MCA can not be compatible with ISA cards, the majorPC makers do not want to be subject to the IBM Then, in 1988, Compaq, AST, NEC, Zenith, Epson, Tandy, Olivetti, Wyse, the Tandy and HP jointly developed 32-bit PC Bus standard ─ ─ EISA (Extended Industry Standard Architecture), and IBM's MCA rival. EISA is superior to ISA PnP (for example, a function), at the same time compatible with ISA cards, but due to the high cost of making EISA only blip in the market.
May 1992 VESA (Video Electronics Standards Association) VL-Bus (VESA Local Bus), a new standard, not only standard ISA-based and backwards-compatible, at the same time to play with the I / O card with a higherperformance, cost more than the EISA low, and therefore can be widely used in the market has been highly anticipated.However VESA only designed for 486CPU design, there is a compatibility problem with the Pentium series; Furthermore VL-Bus buffer, can only support three peripheral slots and has no PnP function; plus VL-BUSnormative standards has not been widely recognized scalability limitations, so the VL-Bus 486CPU using, but have been gradually phased out after the launch of the PCI Bus and Pentium series Intel-led.
Apart from the Intel-led PCIv1.0 Bus (peripheral component interconnect) began sweeping the market, from the PCI Bus support 32bits/33MHz massive transfer speed increase to 1Gbps start, PCI Bus standard Evolution, is the response to and meet the surroundingthe development needs of the device interface and display large amounts of data transfer card, representing escalating transmission speed and increase the bandwidth of the evolutionary history of the the PCI series has also become Bus specification mainstream choice.Self-the PCI v2.0/v2.1 1996 1995 USB v1.0/1.1; 1999 PCI v2.2, Low Profile PCI, PCI-X, Mini-PCI, etc. are bringing eliminating the old ones;1999 to meet the amount of server data processing, PCI 2.2, increasing the power management features and hot-swap technology, and speeds up to 8.5Gbps (1GB / s, 64bits/133MHz) PCI-X1.0; or2002, the maximum transfer speeds of up to 34Gbps (4.2GB / s 64bits/533MHz) PCI-X2.0, are under the evolutionary history of innovation product.
Both PCI transmission architecture are able to enhance higher broadband transmission speed and capacity, but can not achieve the audio and video graphics and other multimedia data transmission quality is clear and resolve the degree of fine or not quality assurance; Moreover, the PCI architecture can not cope with the manyhigh-speed transmission and wireless communications peripherals, such as Fiber channel, Gigabit Ethernet, Serial ATA, Graphics and other applications, in addition to the PCI Bus specifications have different choices.Graphics card Bus terms, in order to improve the PCI efficiency in 1997, Intel raised by the data width of 32 bits, the frequency is 66 MHz AGP v1.0 (Advanced Graphics Port; later officially named as the Accelerated Graphics Port) specification, as well as current launchtransmission speed rate up to 2.1GB / s (32bits/533MHz) AGP 8x, is specifically for the display card design belongs to the dedicated bus between the graphics chip and system chipset.Other Although there are the ALi using HyperTransport (maximum transmission speed of up to 6.4GB / s), Intel used HubLink (266MB / s) support SiS use MuTIOL (to support 1.2GB / s), as well as VIA used VLink(supports 533MB / s) technology flourishing of, but these are just a glimpse, "each blow a tune, or unable to meet the speed, capacity, quality and integration of multiple, improve performance as one of the desire.
Want to meet the the Universal Bus standard interface to different market needs emerged. April 17, 2002, by Intel, ATi, AMD, IBM, HP, Microsoft, TI PCI-SIG (PCI Special Interest Group) announced that the Bus interface standards for the next generation of 3GIO (Third Generation Input Output), is the formulation of the PCI Express divisions paragraphs, July 22 PCI-SIG announced the PCI Express 1.0 specifications, formal Bus specification to another phase. PCI Express would assume, is how to effectively integrate Bus application specifications subject of long carriage, the ability to turn towards the realm of the Common-Bus.The outcome of the IT industry, government, academic and research from all walks of life everyone will wait and see.
|
